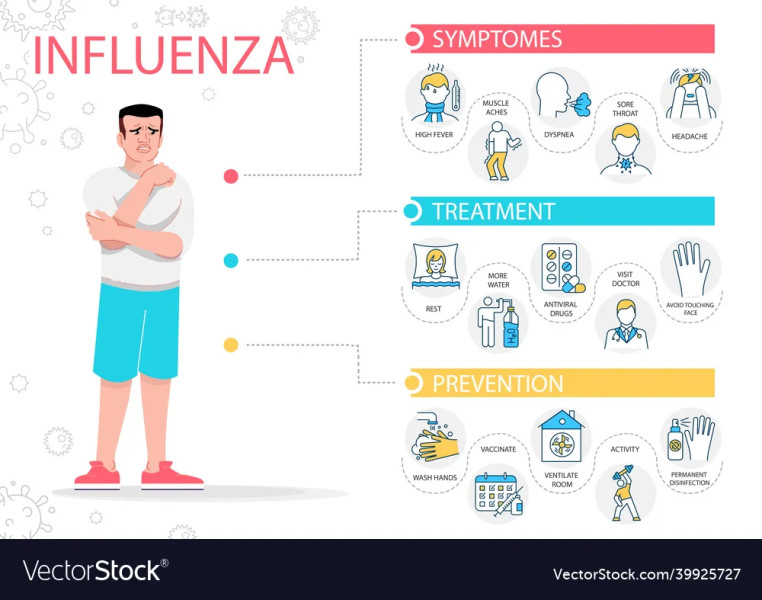
The onset of **flu** season can be a daunting time for many, as the virus spreads rapidly and symptoms can vary widely. Influenza A, a subtype of the influenza virus, is particularly notorious for causing severe respiratory illnesses. Understanding the symptoms of Influenza A is crucial for early detection and effective management. This guide will delve into the common symptoms, how they evolve, and what you need to know to stay informed and protected.
Influenza A is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza A viruses. It is one of the most common strains of the flu virus, responsible for seasonally recurring outbreaks and occasional pandemics. The symptoms of Influenza A can vary from mild to severe, and in some cases, can lead to serious complications. The most common symptoms include a sudden onset of fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, muscle or body aches, headaches, and fatigue. These symptoms can appear abruptly and may last for several days to a couple of weeks. Fever often resolves within a few days, but coughing and fatigue may persist.
One of the distinguishing features of Influenza A is the rapid onset of symptoms. Individuals often experience a sudden high temperature along with general aches and pains, a dry, chesty cough, and a sore throat. This abrupt onset can be a key indicator that the illness is more than just a common cold. Tiredness and weakness are also common, and these symptoms can be particularly debilitating, making it difficult for individuals to carry out their daily activities.
For those who may be wondering how the flu progresses, a day-by-day guide can be helpful. Typically, the flu stages evolve over five to seven days after symptoms appear. Initially, symptoms like fever and body aches are prominent, often peaking within the first few days. As the fever subsides, other symptoms such as coughing and fatigue may persist, sometimes for a week or more. This prolonged period of discomfort can be challenging, and it is essential to manage symptoms effectively to avoid complications.
Children, in particular, may exhibit additional symptoms such as decreased appetite, which can be a concern for parents. Keeping an eye on their hydration and nutritional intake is crucial during this time. Other symptoms in kids may include muscle and body aches, runny or stuffy nose, and headache, which can be similar to those experienced by adults but may present with varying severity.
If you suspect you have Influenza A, it is important to seek medical attention, especially if symptoms are severe or if you are in a high-risk group, such as the elderly, young children, or those with underlying health conditions. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Complications from the flu can include ear or sinus infections, pneumonia, and in severe cases, hospitalization may be required.
In conclusion, being aware of the symptoms of Influenza A is the first step in protecting yourself and others. By recognizing the signs early and taking appropriate measures, you can mitigate the impact of the virus and promote faster recovery. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize your health during this flu season. For more detailed information on flu symptoms and management, you can refer to reliable sources such as the CDC, Mayo Clinic, and other health organizations.