The recent dramatic shifts in Lake Erie water levels have captured public attention, highlighting a natural phenomenon known as a seiche. This event, driven by strong winds, can cause significant changes in lake levels, exposing lake beds and flooding shorelines in a matter of hours. This article will delve into the nature of seiches, their impact on Lake Erie, and the scientific principles behind this fascinating occurrence.
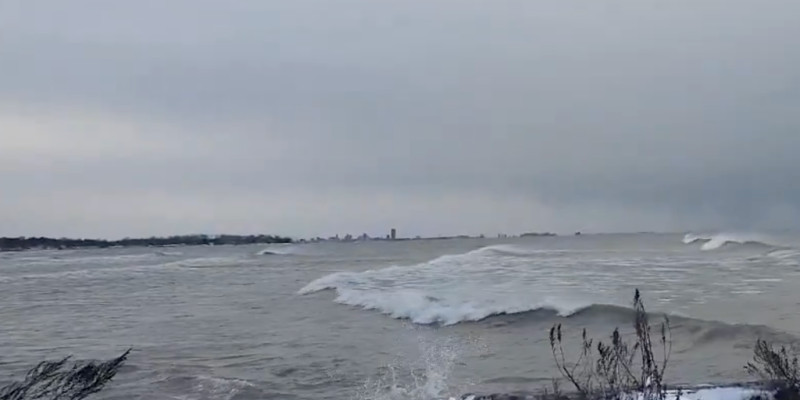
Strong winds from Winter Storm Ezra triggered a dramatic seiche on Lake Erie, sending water surging up to one end of the lake while exposing the lakebed on the other.
A seiche, pronounced "say-sh," is a standing wave in an enclosed or partially enclosed body of water. It is typically caused by strong, sustained winds that push water from one end of the lake to the other, resulting in a sloshing motion. When the wind subsides, the water can oscillate back and forth for hours, creating a seesaw effect on the lake's surface.
Lake Erie is particularly prone to seiches due to its relatively shallow depth and east-west orientation. The lake's elongated shape and shallow waters make it susceptible to wind-driven oscillations, which can lead to significant water level changes. In fact, the lake saw a seiche earlier this fall, demonstrating its vulnerability to this phenomenon.
The recent seiche on Lake Erie was particularly dramatic, with water levels dropping by several feet at one end of the lake while rising by the same amount at the other. This dramatic shift in water levels exposed lake beds that are typically submerged, revealing items that are usually underwater.
Powerful wind gusts from a low-pressure system are producing a seiche in Lake Erie and the Maumee River.
This phenomenon can have significant implications for communities along the shoreline. In an extreme example in 1844, a 22-foot seiche breached a 14-foot seawall at Buffalo, New York, and killed 78 people, highlighting the potential danger of this natural event.
The Lake Erie seiche caused by strong winds can be dangerous. Extreme winds have caused Lake Erie to drain at one end and flood parts of Buffalo, New York, at the other, in what meteorologists describe as a seiche. On Monday, winds from the southwest towards.
Understanding and predicting seiches is crucial for coastal management and public safety. Meteorologists and scientists use advanced modeling techniques to forecast these events, helping communities prepare for potential impacts. As climate change continues to influence weather patterns, the frequency and intensity of seiches may increase, making it essential to stay informed and vigilant.
In conclusion, the recent seiche on Lake Erie serves as a reminder of the dynamic and sometimes unpredictable nature of our natural world. By understanding the science behind this phenomenon, we can better prepare for and mitigate its potential impacts, ensuring the safety and resilience of communities along the shores of Lake Erie.